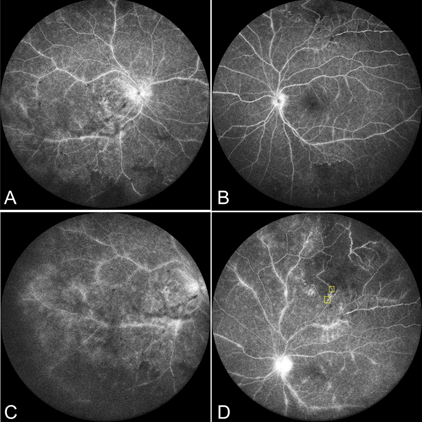
A typical features in Irvan syndrome demonstrated on multimodal imaging
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this work was to describe idiopathic retinal vasculitis, aneurysms, and neuroretinitis (IRVAN) syndrome in a 32-year-old male.
Methods: Case report.
Case report: A 32-year-old male presented with acute visual disturbance. Multimodal imaging revealed retinal vasculitis, aneurysms and neuroretinitis in addition to vitreous inflammation, retinal ischemia and epiretinal membrane. Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) demonstrated multiple microaneurysm in both eyes.
Conclusion: Multimodal imaging was helpful in diagnosing and differentiating IRVAN syndrome from other similar- looking clinical entities. Retinal aneurysms and retinal ischaemia were detectable by fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA). However, OCTA showed multiple microaneurysms that were not clearly differentiable by FFA because of vitreous inflammation and vascular leakage .Microaneurysms in IRVAN syndrome area previously unreported observation. OCTA may help detect thesechanges with accurate details.
Copyright ©2021. All rights reserved.